背景
プログラミングテストの練習問題として、
連結リストを用いたAdd Two Numbers問題を
解いたので、その解法をメモしておく。
目次
連結リスト関連の類題
これまでに解いてきた連結リスト関連の問題はこちら。
問題
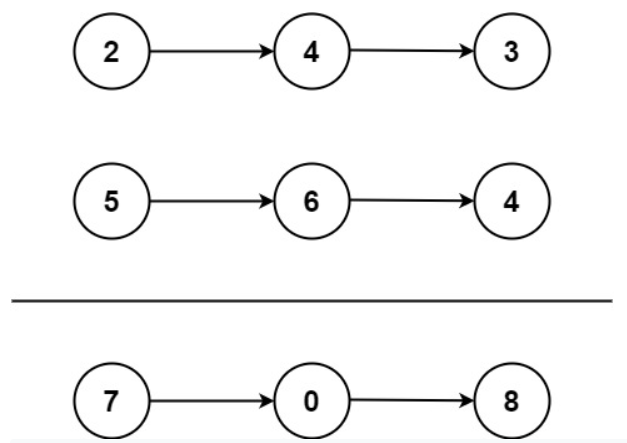
この図のように、複数桁の正の整数に見立てた2つの連結リストが
あるとする。これらはそれぞれReverse Orderで並んでおり、
342, 465といった正の整数を表す。
そして、これらを足すことで得られる807という整数を
Reverse Orderの連結リストで表した7->0->8を出力させる
ようなアルゴリズムを実装する。
解法
下記のステップで実行されるアルゴリズムとなる。
- 現在の参照ノードをダミーのheadノードで初期化
- 次の桁に繰り上げる分をcarryとし、それを0で初期化
- 入力する二つのリストをl1, l2とし、その先頭ノードへのポインタをp, qとする
- l1, l2がともに終端に到達するまで以下の処理を繰り返す
4-1. 参照しているノードpの値を変数xに格納。もしpが終端なら0を格納
4-2. 参照しているノードqの値を変数yに格納。もしqが終端なら0を格納
4-3. 一つ前のノードからの繰り上げを加味した合計値sum = x + y + carryを計算
4-4. carryの値を更新: sum / 10
4-5. 値(sum % 10)を持つ新しいノードを作る
4-6. 作ったノードのポインタを、現在の参照ノードの次に来るとしてnextにセット
4-7. 参照するノードを次のnextに進める
4-8. ノードp, qも次に進める - 最後に計算されたcarry値が1なら、その繰り上げ分の新しいノードを作る
- ダミーのheadノードのnextノードポインタを返す
このアルゴリズムを実装したC++サンプルコードはこのようになる。
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; Node *next; Node() : data(0), next(NULL) {} Node(int x) : data(x), next(NULL) {} Node(int x, Node* next) : data(x), next(next) {} }; void push(struct Node **head, int new_data) { // allocate node Node* new_node = new Node(); // put in the data new_node->data = new_data; // link the old list off the new node new_node->next = (*head); // move the head to pointer to the new node (*head) = new_node; } Node* add_two_numbers(Node* l1, Node* l2) { Node* dummy_head = new Node(0); Node* p = l1; Node* q = l2; Node* current = dummy_head; int carry = 0; while (p != NULL || q != NULL) { int x = 0; if (p != NULL) x = p->data; int y = 0; if (q != NULL) y = q->data; int sum = x + y + carry; carry = sum / 10; current->next = new Node(sum % 10); current = current->next; if (p != NULL) p = p->next; if (q != NULL) q = q->next; } // end of list if (carry > 0) current->next = new Node(carry); return dummy_head->next; } int main(void) { // create input linked list: l1 Node* l1 = NULL; push(&l1, 3); push(&l1, 4); push(&l1, 2); // create input linked list: l2 Node* l2 = NULL; push(&l2, 4); push(&l2, 6); push(&l2, 5); Node* result = add_two_numbers(l1, l2); // print data of each node while (result != NULL) { cout << result->data << endl; result = result->next; } return 0; }
このとき、二つの入力l1, l2のノード数をそれぞれm, nとすると、
計算時間はO(max(m, n))と見積もれる。
