目的
前回の記事で書いたように、数年ぶりにROSを使う機会がありました。
その機会の中で、屋外でLiDARが埃やその他ノイズを検知したときの
点群をフィルタリングするプログラムを作ったので、そのアルゴリズム
とその性能検証、ソースコードについて紹介しようと思います。
目次
- 目的
- 目次
- 目標設定
- Occupancy Grid Mapの利用
- 地図を構築するためのパラメータ
- 3次元点が所属するセルのインデックス計算
- 各セルに属する物体の高さ推定
- ベイズの定理による占有確率の更新
- 対数の性質を利用した確率更新の計算
- 占有確率に関するパラメータ
- 占有確率に基づくフィルタリング性能の検証
- ROSプログラムの設計とソースコード
- まとめ
目標設定
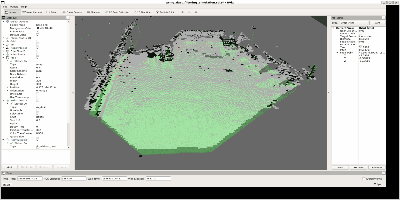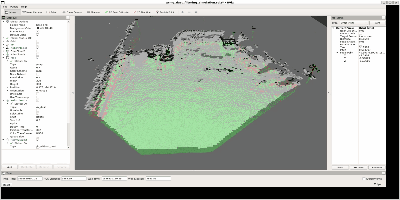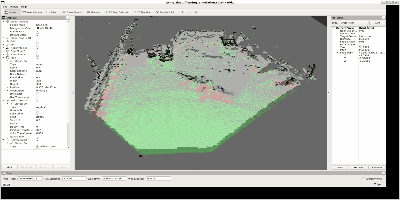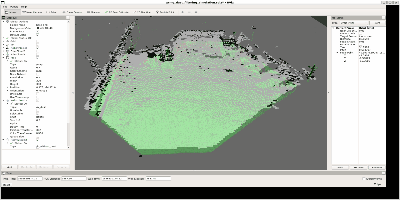
フィルタリングする前の点群はこのようなものです。
これは1台のLiDARを固定した状態で目の前の環境をスキャンしたものであり、
障害物になり得る大きな静止物体、移動物体、地面、埃などのノイズといった
ものが含まれています。
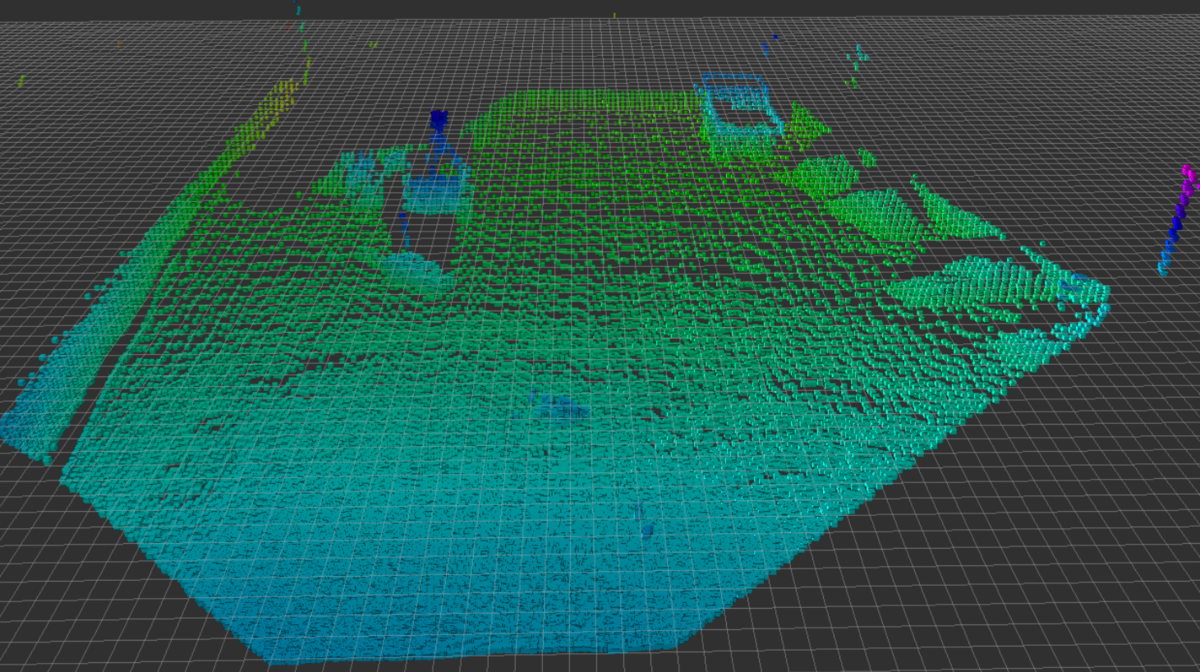
これらの中から埃のようなノイズを除去することが第一の目標ですが、
それに伴って除去すべきでないものまで無くしてしまうのは良くありません。
そこでまずは、本当に除去すべき対象を何にするか、逆に残すべき対象を
何にするか、という目標設定をします。
残すべき対象①: 大きな静止物体
まず一つ目は、このように障害物になりえる大きな静止物体です。
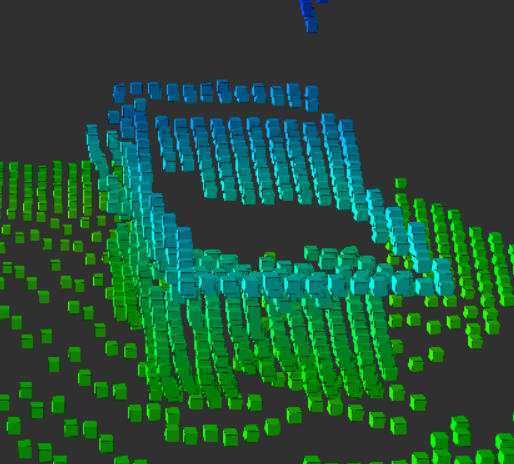
安全な自律移動のためには、これらのような物体を検知した
点群はフィルタリングされずに残す必要があります。
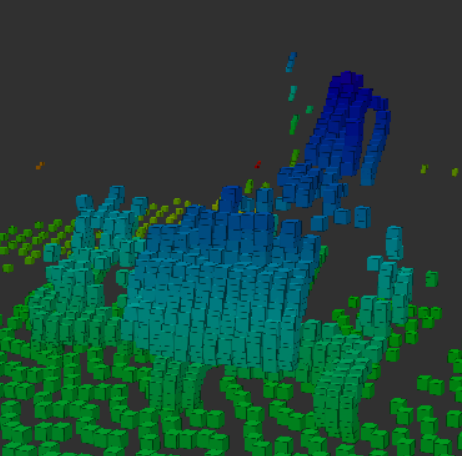
残すべき対象②: 移動物体
二つ目はこのような移動物体です。ただし、今回のデータに含まれる
移動物体は、移動しながら埃を巻き上げていくため、移動物体自身の
点群と埃の点群が混在した状態になります。
これを埃とだけ捉えるなら丸ごとバッサリ除去するだけですが、
同時に移動物体でもあるので、障害物として検知されるべきもの
でもあります。
そのため、この物体に関しては、移動物体であるということが
分かる程度に点群を残しつつ、周囲の巻き上がった埃を出来るだけ
除去するように微調整が可能なアルゴリズムにするという方針を
取ります。
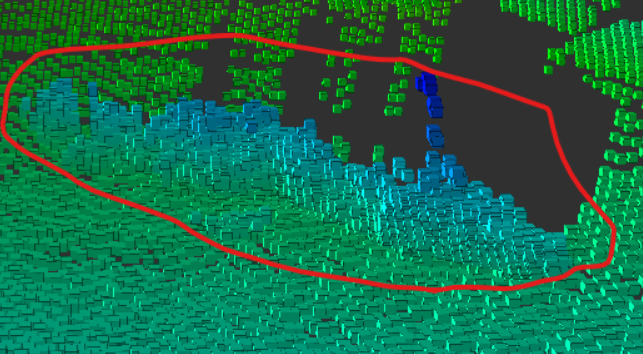
残すべき対象③: 地面
三つ目はこのような地面です。
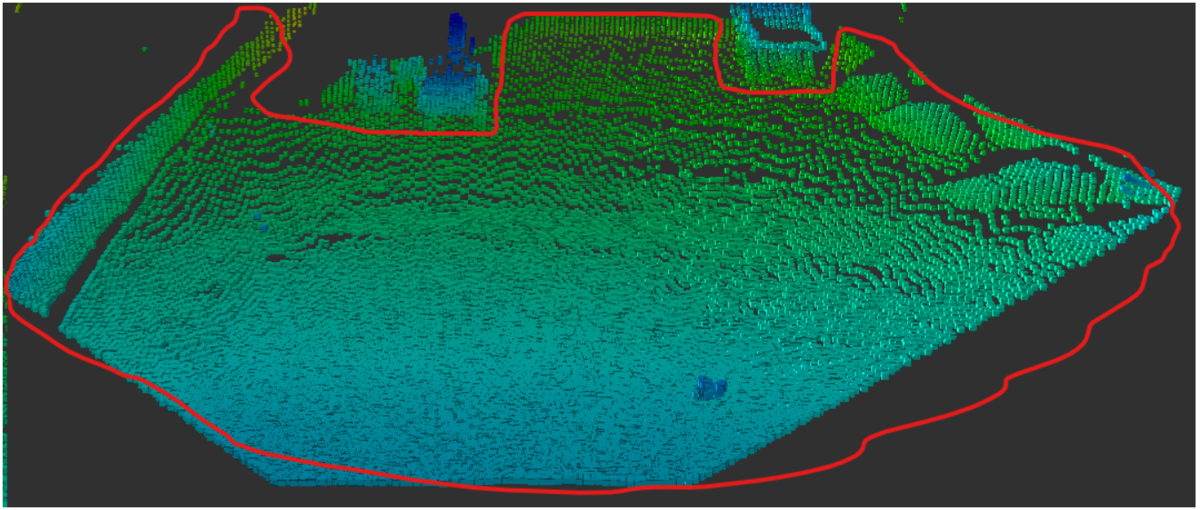
公道での自動運転で走行するような路面と違い、この地面には
平坦に近い部分と凹凸のある部分が混在しているのが特徴です。
全てが平坦であればバッサリ除去して無視すればいいですが、
凹凸がある部分はロボットや車両自身を傷つける可能性がある
ので無視すべきではありません。
なのでここでは地面は残すべき対象とし、凹凸のある部分と
平坦な部分を区別できるようにします。
除去すべき対象: 上記以外の埃やその他ノイズ
最後は、上記で述べてきた物以外の埃やノイズです。
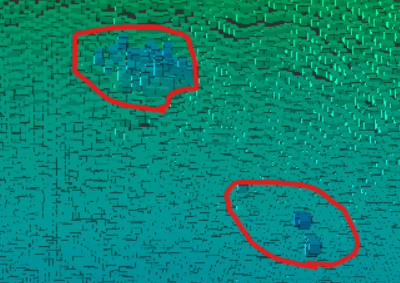
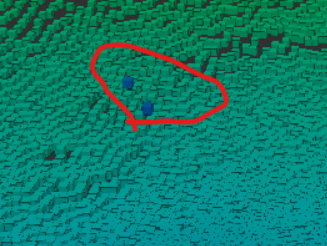
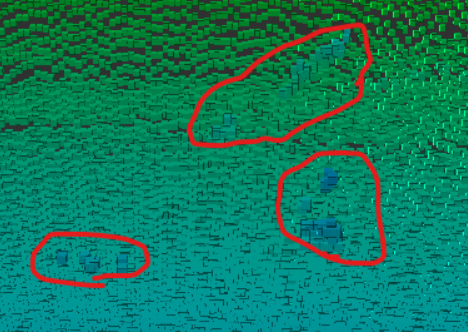

上記の残すべき対象①~③を出来るだけ残しつつ、
これらを上手く除去するアルゴリズムを検討します。
Occupancy Grid Mapの利用
今回の除去の対象となる埃というのは、同じ場所に現れ続ける
のではなく、風などによって移動する、またチラチラと出たり
消えたりする、という特徴があります。
こういった特徴から、検知した各物体の空間上での存在を確率で
表現する占有格子地図(Occupancy Grid Map)を利用すれば、その
存在確率に応じて埃かそうでないかを判定できるのではないかと
考えました。
Occupancy Grid Mapについての説明は、こちらの動画が
分かりやすくておススメなので参照ください。
地図を構築するためのパラメータ
上記の動画を見れば分かるように、Occupancy Grid Mapは
その名の通り、空間を2次元の格子状に区切り、各格子(セル)内に
どれだけの確率で物体が存在するかを逐次計算するものです。
そのため、その地図全体のサイズや原点、格子のサイズ(地図の
解像度)などをパラメータとして事前に設定する必要があります。
今回構築する地図は、こちらのようなパラメータを持ちます。
- 解像度:
]
- 幅:
]
- 高さ:
]
- 地図の中心座標:
- 地図の原点座標:
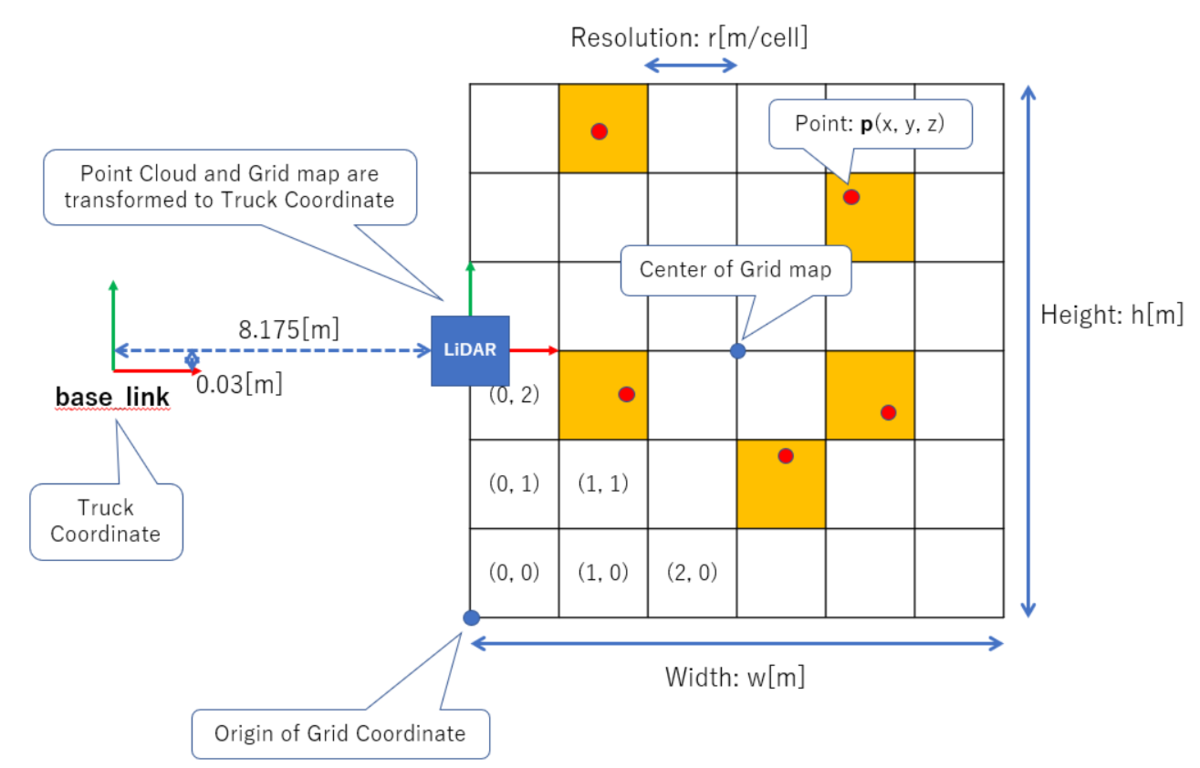
そしてこの時、LiDARの点群や地図の中心座標、原点座標は
全て図中のbase_link座標系を基準とし、地図上の各セルの
インデックスは、地図の左下を基準とするようにします。
3次元点が所属するセルのインデックス計算
LiDARが各時刻でスキャンした点群に含まれるある3次元点を
とし、それが属するセルのインデックスを
とすると、
と
はそれぞれ下記の式で計算できます。
ここまでだと、Occupancy Grid Mapを2次元の配列で表現する
ことになりますが、最後にこれを1次元のベクトルで表現した
場合のインデックスを下記の式で計算します。
これは、ROSでGrid Mapを扱う際に型であるnav_msgs::OccupancyGridが
各セルを1次元のベクトル上に並べたものとして扱うようになっている
ためです。
また、このように1次元のベクトル上に並べる順番として、列優先順
(Column-major order)と行優先順(Row-major order)の2種類があり、
上記の計算式はRow-major orderに当たります。
各セルに属する物体の高さ推定
上記のインデックス計算により各3次元点がどのセルに属するかが
求まったら、各セル内の最新の2点の座標の差分を取ることで、
そのセルに属する物体の高さ情報を推定します。
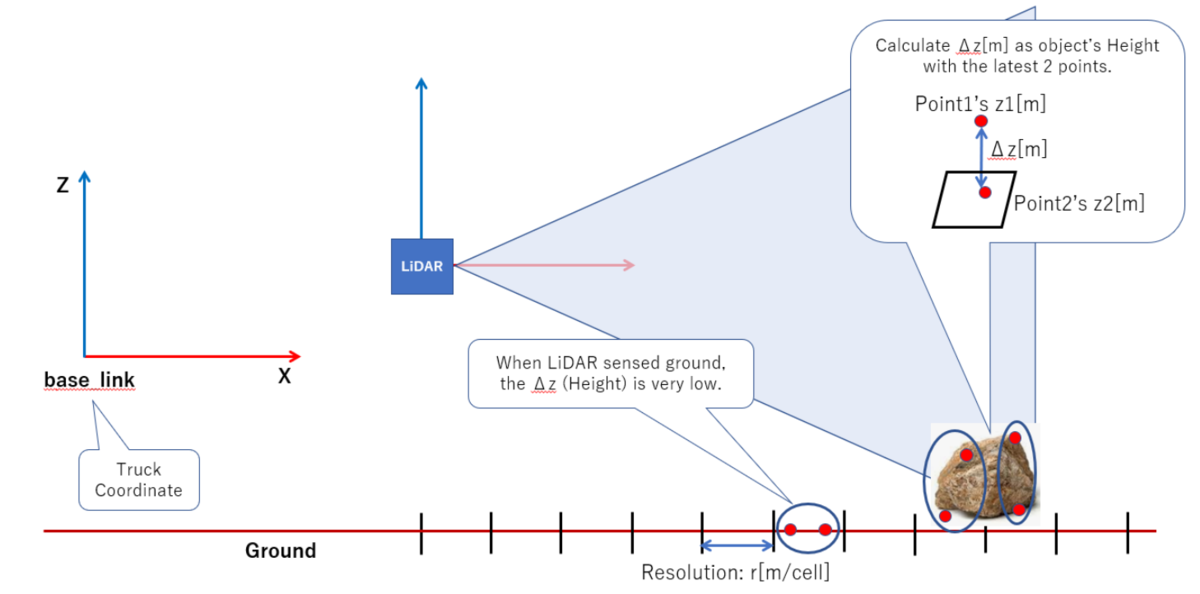
今回はこの高さ情報に0.1mという閾値を適用し、これを超えたら
障害物になる可能性があるものと考えるようにします。
ベイズの定理による占有確率の更新
高さが閾値0.1m以上であるなら、そのセル内には障害物が存在する
可能性があるとして、そのセルにおける占有確率を更新します。
そして、その占有確率の更新にはこちらの記事で解説されている
ようなベイズの定理を利用します。
ベイズの定理による占有確率の更新式はこのようになりますが、
これを今回のような障害物の占有確率の更新に適用する場合、
上記の式中の各値をそれぞれ下記のように定義されます。
: セル
内の物体が障害物である確率
: 物体の高さが閾値0.1m以上である確率
: 障害物である物体の中で高さ0.1m以上の物が占める割合
: セル
内の物体の高さが0.1m以上、かつ障害物である確率
この時を事前確率、
を尤度、
を事後確率
といいます。また、は周辺尤度といい、
という式で計算されます。これは、障害物である物体の中で
高さが0.1m以上となる物の割合と、障害物でない物体の中で
高さが0.1m以上となる物の割合の和となります。
ここまでの説明をまとめると、今回の問題における占有確率の
更新というのは、一時刻前までに計算された確率に、
センサから観測された物体の高さ情報に基づいた尤度の比
を掛け合わせることで、センサの観測情報を考慮した新たな
確率に更新するということになります。
こうして求められた確率を閾値処理することで、
それが埃のようなノイズなのか、障害物なのかを判定する
ようにします。
対数の性質を利用した確率更新の計算
今回のアルゴリズムを実装したプログラムでは行っていませんが、
確率の値は0~1を取り、それを掛け算により更新していくため、
0.9999999などのように桁数が多くなり桁落ちが発生するという
問題があります。
そのため、確率の値の対数を取ることで処理する値の桁数を
抑える、また対数の性質から掛け算を足し算として計算できる
ようになるため、計算負荷も軽くなるというやり方があります。
占有確率に関するパラメータ
Grid Mapを初期化する際には、更新前の事前確率であるは、
各セルにおいて0.5とします。これは、センサからの情報が何もない
状態では、そこに障害物があるかどうか分からない不明であるため、
確率を半々の50%にするという意味です。
また、尤度に当たると
は言わば重みであり、
本来であればこれを統計的に決定する必要があります。
ただし、今回はそれを決定できるような十分なデータが
無かったので、経験的に次のように設定しました。
そして、最終的に更新された占有確率であるに応じて
次のように判定します。
- 0.5 <
: 障害物になり得る物体
- 0.1 <
<= 0.5: 埃、その他ノイズ
: 障害物になり得ない物体
占有確率に基づくフィルタリング性能の検証
ここまで説明してきたアルゴリズムにより、埃やその他ノイズの
点群をどの程度除去できるのか検証してみました。
Grid Mapの初期化
まずはLiDARで物体を検知する前のまっさらな地図を作ります。
このときの各セルの占有確率は0.5であり、その状態ではこの
ようなグレーに色付けされた地図になります。

占有確率の更新
そして、今回構築したアルゴリズムによって占有確率を更新した
ときの地図はこのようになります。
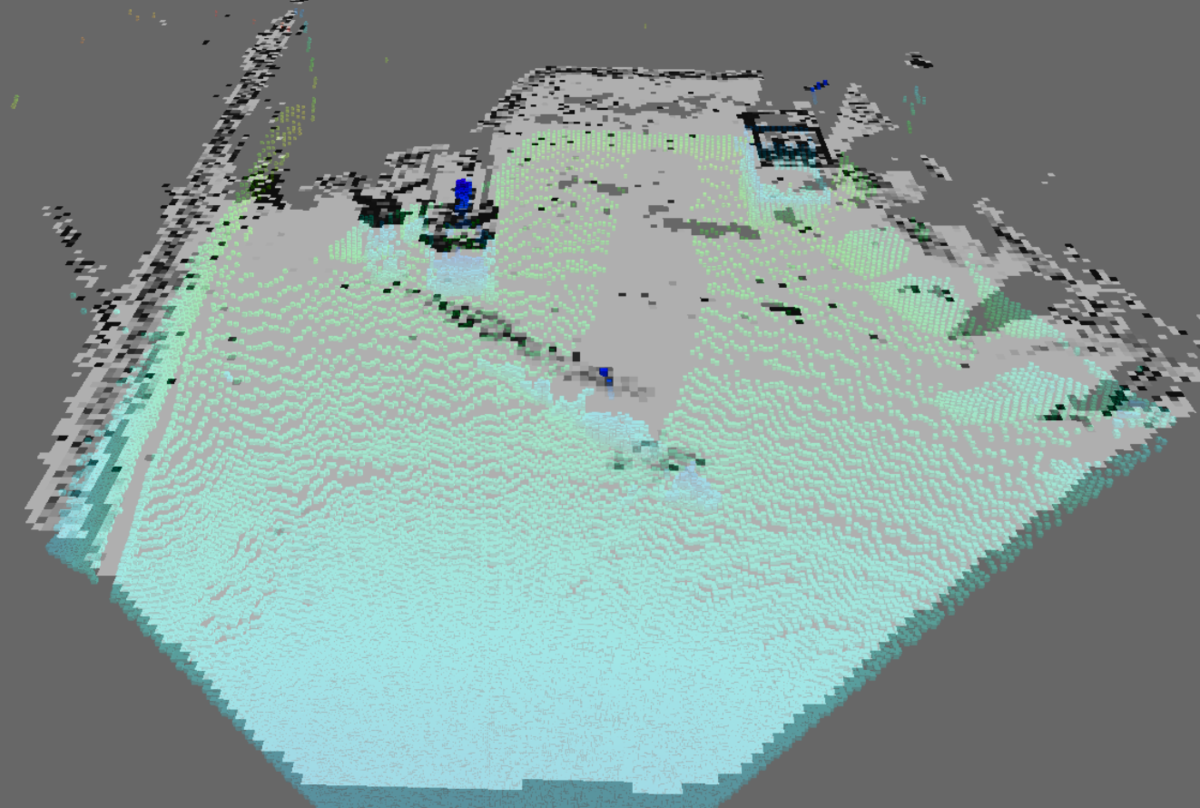
占有確率が高くなるほどセルの色は黒く、低くなるほど白く
なっていきますが、本記事の冒頭で決めたように、障害物に
なり得る物体があるセルの占有確率は高く、
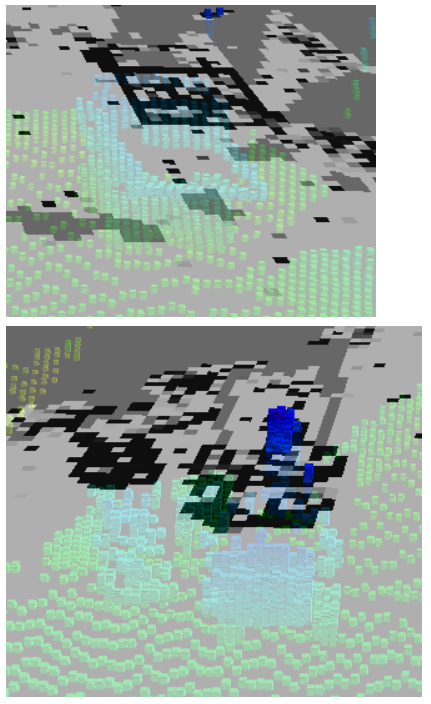
埃やノイズのようにチラチラとした現れない物体があるセルの
占有確率は比較的低めに更新されていることが分かります。
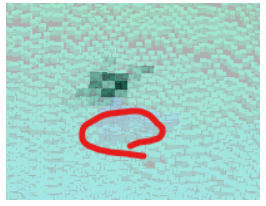
また、今回一番扱いが難しい移動物体に対しては、このように
占有確率が高い部分と低い部分が混在するような更新になります。
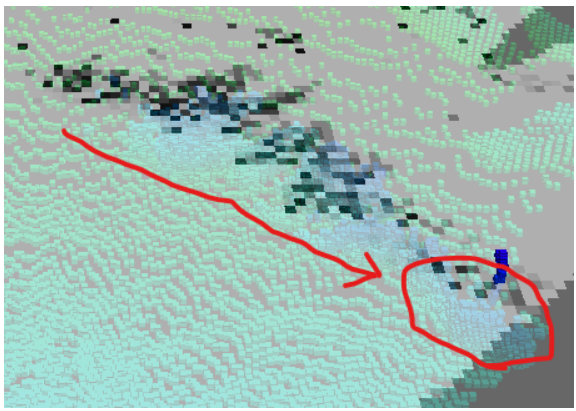
これにより、障害物としての点群はある程度残しつつ、
埃やノイズとしての点群は除去するということができる
ようになっていることが分かります。
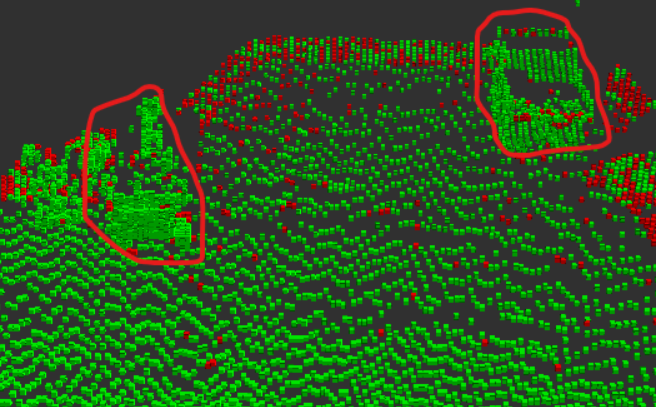
埃+ノイズとそれ以外の点群の区別
次に、更新された占有確率に基づいて、埃やノイズの点群と
それ以外の障害物や地面などの点群を区別できるか確認して
みました。前者を赤、後者を緑で色分けした結果、このように
なりました。
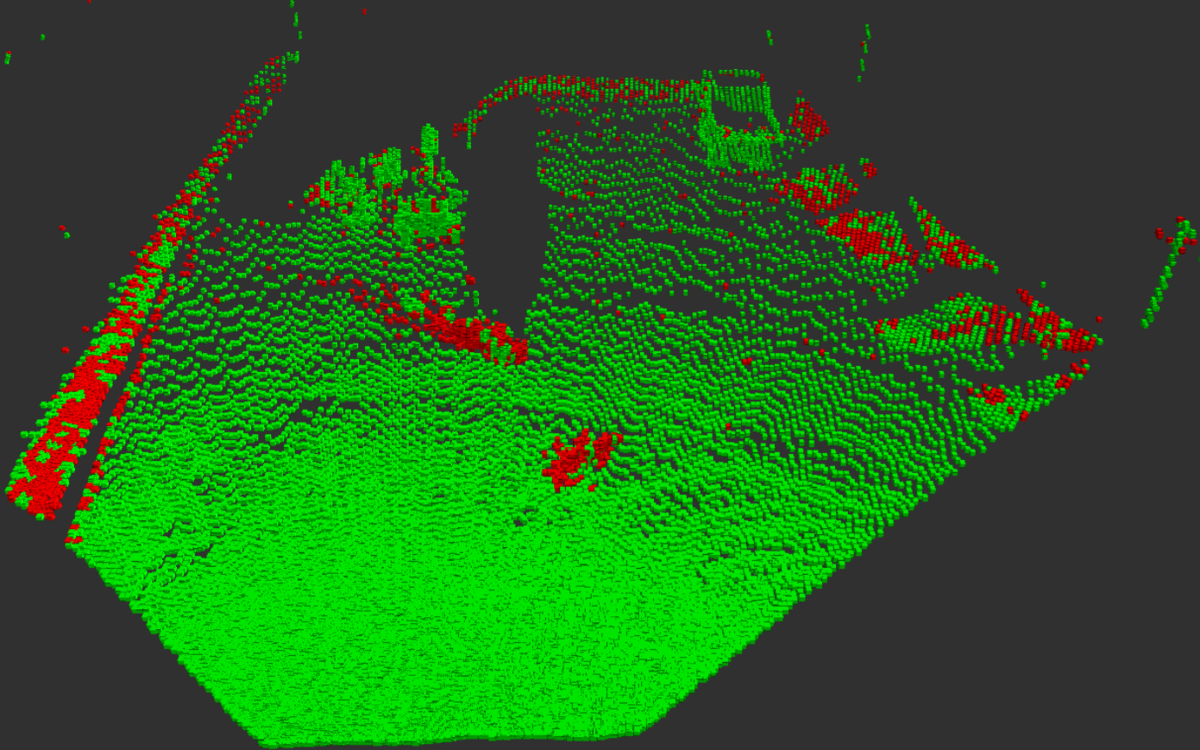
埃やノイズを表す赤色の点群が地面などを表す緑色の点群に
混ざっているため、さすがに完全に区別することはできません
でした。
それでも、このように大体の埃やノイズは赤色になり、
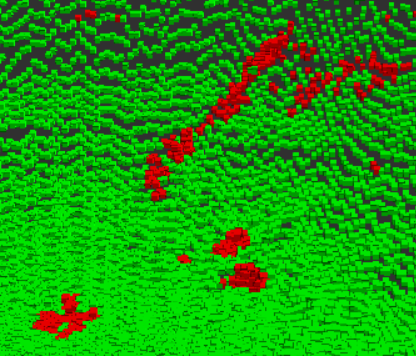
大きな障害物や地面などは緑色になっていることが分かります。
埃とノイズの点群の除去
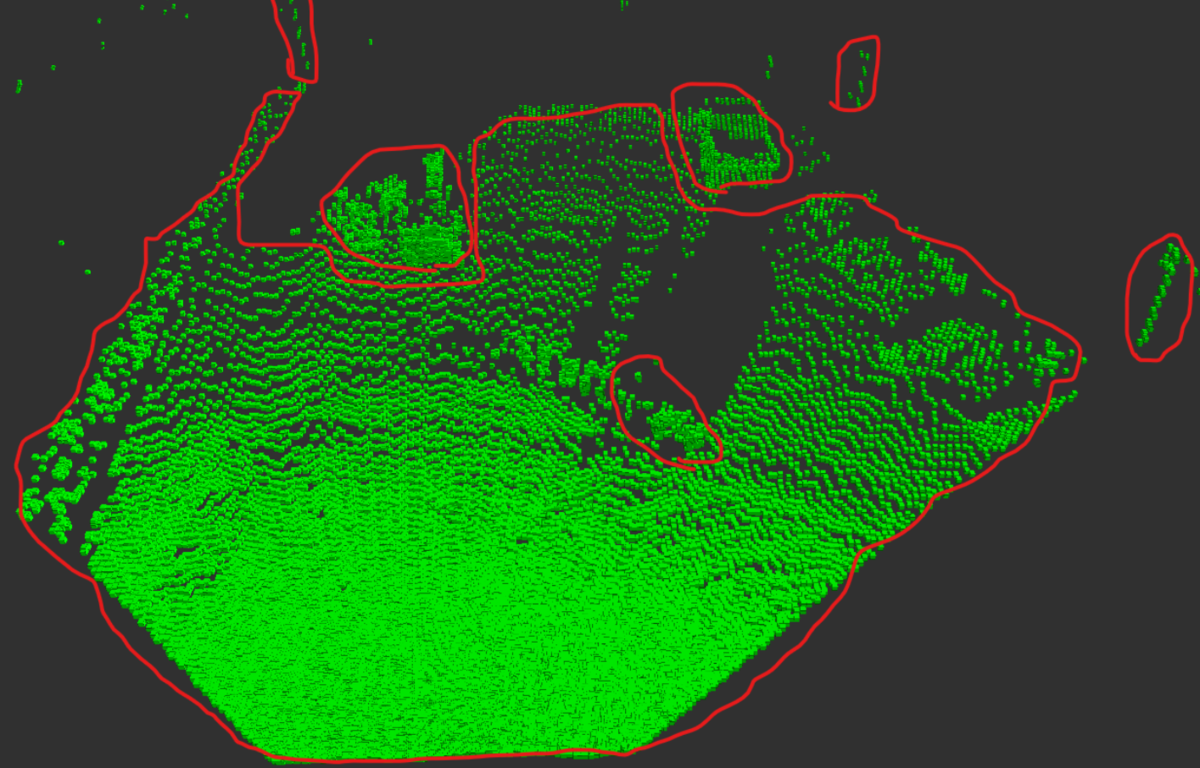
最後に、上記で区別した赤色の点群を除去した際の
残りの緑の点群を確認してみました。決して完璧では
ないですが、このように最初の目標設定の通りに残したい
点群の大部分は残すことが出来ました。
ROSプログラムの設計とソースコード
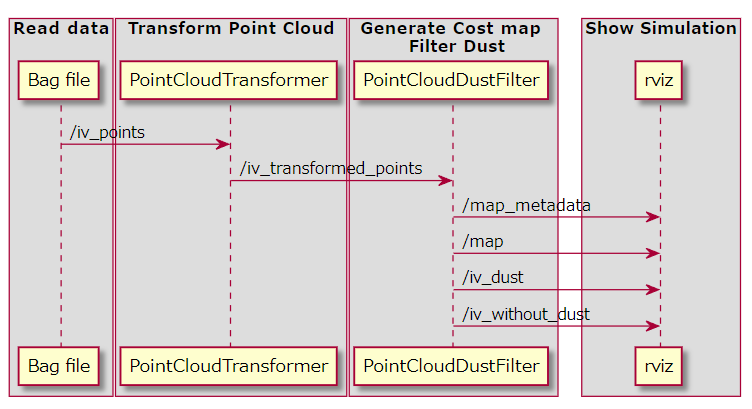
今回構築した上記のアルゴリズムを実行するプログラムの
処理はこちらのような流れで動きます。
点群を座標変換するPointCloudTransformer
まずはROSのbagファイルから読み取ったポイントクラウドの
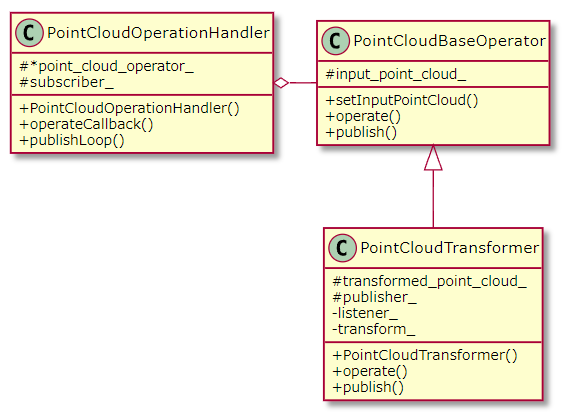
座標点をbase_link基準に座標変換するノードを作ります。
こちらがクラス図ですが、基本的にはポイントクラウドを処理
するための抽象クラス(PointCloudBaseOperator)を用意し、それを
継承することで座標変換クラスを実現します。
そして、それをポイントクラウド処理のフレームワーククラス
(PointCloudOperationHandler)に渡すことで一連の処理が
実行されます。
その処理の流れはこちらのシーケンス図のようになります。
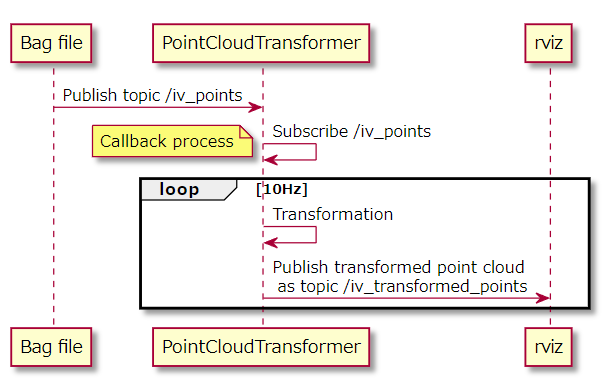
そしてこちらがC++ソースコードです。
/** * @file point_cloud_transformer.cpp * @author Shisato Yano (shisatoyano@gmail.com) * @brief Class for transforming point cloud data * @version 0.1 * @date 2022-07-02 * * @copyright Copyright (c) 2022 * */ #include <pcl_ros/transforms.h> #include "point_cloud_operation_handler.hpp" #include "point_cloud_transformer.hpp" PointCloudTransformer::PointCloudTransformer(ros::NodeHandle &nh) { publisher_ = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("iv_transformed_points", 10); } void PointCloudTransformer::operate() { // from sensor coordinate to truck coordinate, base_link pcl_ros::transformPointCloud("base_link", transform_, input_point_cloud_, transformed_point_cloud_); } void PointCloudTransformer::publish() { // exception process to receive transformation info try{ listener_.lookupTransform("base_link", "innovusion", ros::Time(0), transform_); } catch(tf::TransformException &ex){ ROS_ERROR("%s", ex.what()); } publisher_.publish(transformed_point_cloud_); } /** * @brief Main process of this Node * * @param argc * @param argv * @return int */ int main(int argc, char **argv) { ros::init(argc, argv, "point_cloud_transformer"); ros::NodeHandle nh; // subscribe topic "iv_points" as input point cloud PointCloudOperationHandler handler(nh, new PointCloudTransformer(nh), "iv_points"); // publish transformed point cloud handler.publishLoop(); return 0; }
埃やノイズを除去するPointCloudDustFilter
続いて、座標変換されたポイントクラウドからGrid Mapを
作成し、それによる占有確率更新で埃を除去するクラスを
作ります。
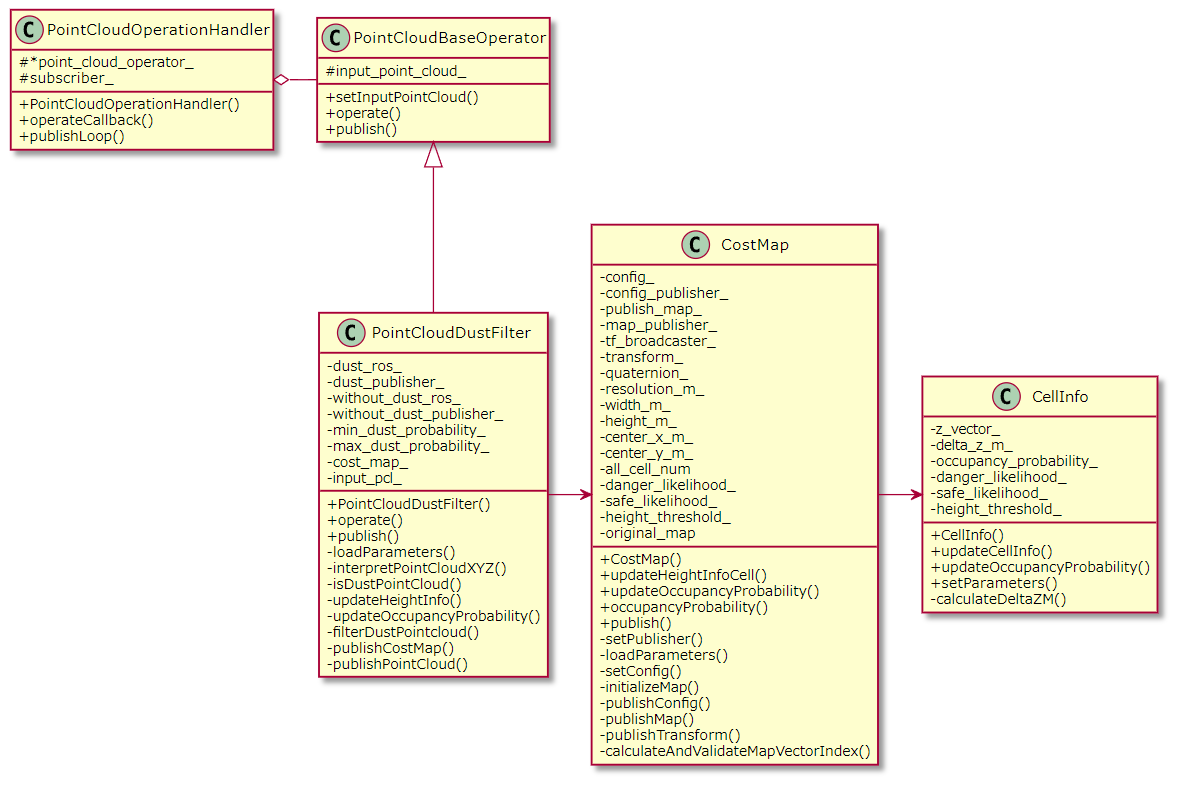
このクラスは、Grid Mapを作成するクラス(CostMap)と、その中の
各セルが持つ情報をまとめるクラス(CellInfo)をメンバに持ち、
それらが持つ各種メソッドをコールすることで、Grid Mapの作成と
確率更新を実行します。
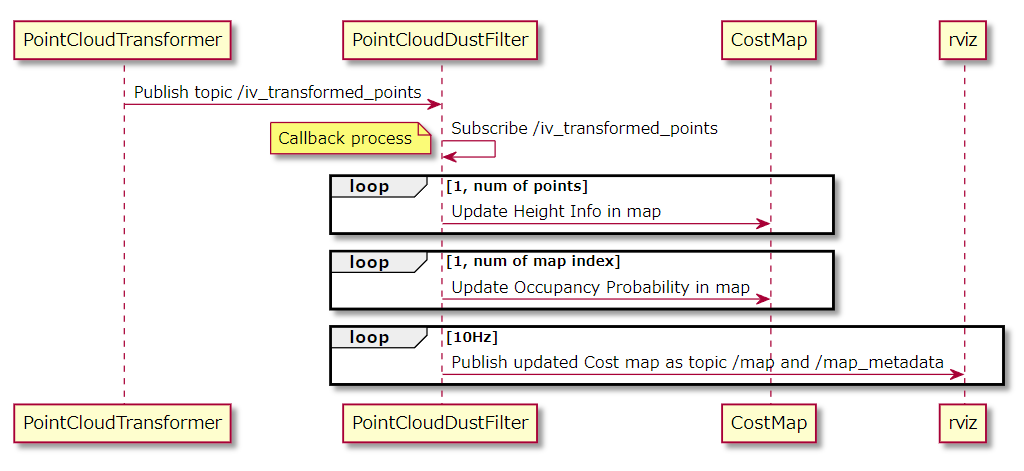
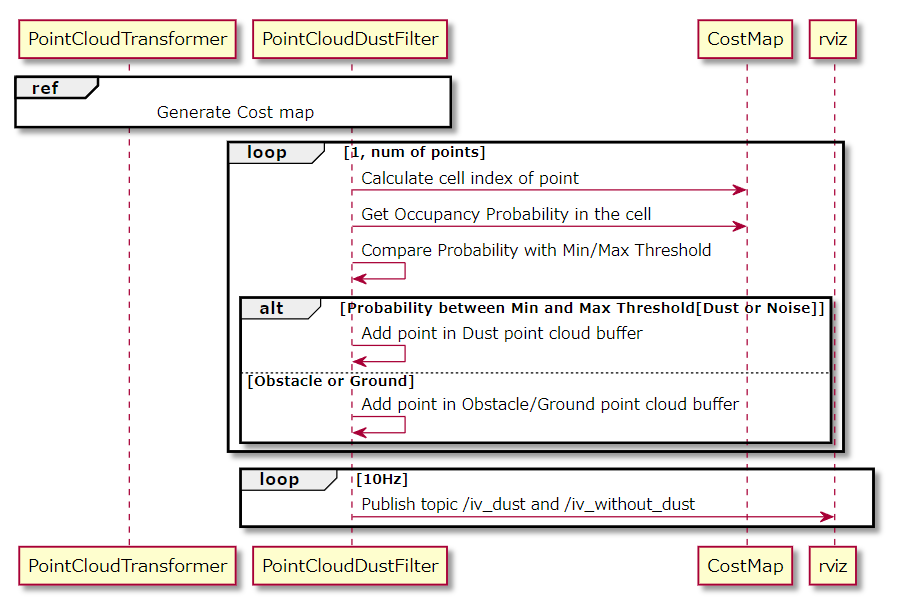
そして、更新した各セルの占有確率に基づき、ポイントクラウドの
フィルタリングを実行します。
最後にソースコードを紹介します。まずこちらが、各セルが
持つ情報やその処理を行うメソッドをまとめたクラスです。
#include <ros/ros.h> #define MIN_PROBABILITY 0.1f #define MAX_PROBABILITY 1.0f #define UNKNOWN_PROBABILITY 0.5f /** * @brief Class for storing data in a cell of grid map * */ class CellInfo { public: /** * @brief Construct a new Cell Info object * */ CellInfo() { delta_z_m_ = 0.0f; // Occupancy probability is initialized 50%. // Before sensor starts working, application can not judge // each cell is danger or safe. occupancy_probability_ = UNKNOWN_PROBABILITY; danger_likelihood_ = 0.0f; safe_likelihood_ = 0.0f; height_threshold_ = 0.0f; } /** * @brief Update data in this cell * Height information in this cell is calculated * @param z_m Z position[m] of point cloud */ void updateCellInfo(float z_m) { calculateDeltaZM(z_m); } /** * @brief Update occupancy probability * This is probability that Danger object is existing in this cell * This probability is calculated by Bayes' theorem */ void updateOccupancyProbability() { float prior, marginal_likelihood_, posterior; prior = occupancy_probability_; marginal_likelihood_ = (danger_likelihood_ * prior) + (safe_likelihood_ * (1.0f - prior)); if (delta_z_m_ > height_threshold_) { occupancy_probability_ = (danger_likelihood_ * prior) / marginal_likelihood_; } else if (delta_z_m_ > 0 && delta_z_m_ <= height_threshold_) { occupancy_probability_ = (safe_likelihood_ * prior) / marginal_likelihood_; } else {} // do nothing // limit probability over than 10% at least // because probability can't be updated by this algorithm if this value is zero if (occupancy_probability_ < MIN_PROBABILITY) { occupancy_probability_ = MIN_PROBABILITY; } else if (occupancy_probability_ > MAX_PROBABILITY) { occupancy_probability_ = MAX_PROBABILITY; } else {} // do nothing } /** * @brief Getter of updated occupancy probability in this cell * This value should be uint8_t to store in map data of ROS * @return uint8_t */ uint8_t occupancyProbability() { return static_cast<uint8_t>(occupancy_probability_ * 100.0f); } /** * @brief Setter of parameters for occupancy probability update * * @param danger_likelihood ratio of object higher than threshold in danger objects * @param safe_likelihood ratio of object higher than threshold in safe objects * @param height_threshold threshold of object's height in this cell */ void setParameters(float danger_likelihood, float safe_likelihood, float height_threshold) { danger_likelihood_ = danger_likelihood; safe_likelihood_ = safe_likelihood; height_threshold_ = height_threshold; } private: /** * @brief Calculate height info of object in this cell * Difference of the latest 2 points's z[m] is defined as height * @param z_m */ void calculateDeltaZM(float z_m) { uint8_t i_1, i_2; z_vector_.push_back(z_m); // at least 2 points should be stored if (z_vector_.size() >= 2) { i_1 = z_vector_.size() - 1; i_2 = i_1 - 1; delta_z_m_ = abs(z_vector_[i_1] - z_vector_[i_2]); z_vector_.erase(z_vector_.begin()); // keep storing the latest 2 points } } std::vector<float> z_vector_; float delta_z_m_; float occupancy_probability_; float danger_likelihood_, safe_likelihood_; float height_threshold_; }; #endif // _H_CELL_INFO_
次に、そのセルクラスで構成されるGrid Mapのクラス。
/** * @file cost_map.hpp * @author Shisato Yano (shisatoyano@gmail.com) * @brief Class for generating Cost map * @version 0.1 * @date 2022-07-02 * * @copyright Copyright (c) 2022 * */ #ifndef _H_COST_MAP_ #define _H_COST_MAp_ #include <ros/ros.h> #include <nav_msgs/MapMetaData.h> #include <nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid.h> #include <tf/transform_broadcaster.h> #include "cell_info.hpp" #include "grid_map_utility.hpp" /** * @brief Class for generating Cost map * */ class CostMap { public: /** * @brief Construct a new Cost Map object * */ CostMap(){} /** * @brief Construct a new Cost Map object * * @param nh Reference of Node handle object * @param pnh Reference of Parameter node handle object */ CostMap(ros::NodeHandle &nh, ros::NodeHandle &pnh) { setPublisher(nh); loadParameters(pnh); setConfig(); initializeMap(); } /** * @brief Update Object's height in a cell of cost map * Height is calculated with the latest 2 points's z_m * @param x_m x position[m] of point cloud * @param y_m y position[m] of point cloud * @param z_m z position[m] of point cloud */ void updateHeightInfoInCell(float x_m, float y_m, float z_m) { uint32_t i_v; // calculate index and validate the index is within map's size // this method return true when calculated index is valid if (calculateAndValidateMapVectorIndex(x_m, y_m, i_v)) { original_map[i_v].updateCellInfo(z_m); } } /** * @brief Update Occupancy probability in a cell of cost map * This is probability that Danger object is existing in this cell * This probability is calculated by Bayes' theorem */ void updateOccupancyProbability() { for (uint32_t i_v=0; i_v < all_cell_num_; i_v++) { original_map[i_v].updateOccupancyProbability(); // calculated probability is set in another map to publish // this map is used for showing in rviz publish_map_.data[i_v] = original_map[i_v].occupancyProbability(); } } /** * @brief Getter of Occupancy probability * * @param x_m position x[m] of point cloud * @param y_m position y[m] of point cloud * @return uint32_t */ uint32_t occupancyProbability(float x_m, float y_m) { uint32_t i_v; // calculate index and validate the index is within map's size // this method return true when calculated index is valid if (calculateAndValidateMapVectorIndex(x_m, y_m, i_v)) { return original_map[i_v].occupancyProbability(); } else // if index is invalid, return minimum probility { return static_cast<uint8_t>(MIN_PROBABILITY * 100.0f); } } /** * @brief Publish data * */ void publish() { publishConfig(); publishMap(); publishTransform(); } private: /** * @brief Setter of Node handle object to publish data * * @param nh Reference of Node handle object */ void setPublisher(ros::NodeHandle &nh) { config_publisher_ = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::MapMetaData>("map_metadata", 10); map_publisher_ = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid>("map", 10); } /** * @brief Load parameters from config file * Config file: config/grid_map_config.yaml * @param pnh Reference of parameter node handle object */ void loadParameters(ros::NodeHandle &pnh) { // for generating cost map pnh.getParam("resolution_m", resolution_m_); pnh.getParam("width_m", width_m_); pnh.getParam("height_m", height_m_); pnh.getParam("center_x_m", center_x_m_); pnh.getParam("center_y_m", center_y_m_); // for updating occupancy probability pnh.getParam("danger_likelihood", danger_likelihood_); pnh.getParam("safe_likelihood", safe_likelihood_); pnh.getParam("height_threshold", height_threshold_); } /** * @brief Setter of each config parameter as initialization * */ void setConfig() { config_.resolution = resolution_m_; config_.height = static_cast<uint32_t>(height_m_/resolution_m_); config_.width = static_cast<uint32_t>(width_m_/resolution_m_); all_cell_num_ = config_.width * config_.height; config_.origin.position.x = center_x_m_ - (width_m_/2.0); config_.origin.position.y = center_y_m_ - (height_m_/2.0); config_.origin.position.z = 0.0; config_.origin.orientation.x = 0.0; config_.origin.orientation.y = 0.0; config_.origin.orientation.z = 0.0; config_.origin.orientation.w = 1.0; } /** * @brief Initialize map's size and probability in each cell * */ void initializeMap() { original_map.resize(config_.width * config_.height); publish_map_.header.frame_id = "map"; for (uint32_t i=0; i < all_cell_num_; i++) { // initialize occupancy probability as 50% in each cell // this mean it is unknown before sensor detect an object publish_map_.data.push_back(static_cast<uint8_t>(UNKNOWN_PROBABILITY*100.0f)); // set parameters for updating occupancy probability in each cell object original_map[i].setParameters(danger_likelihood_, safe_likelihood_, height_threshold_); } } /** * @brief Publish configuration data of cost map * */ void publishConfig() { config_.map_load_time = ros::Time::now(); config_publisher_.publish(config_); } /** * @brief Publish cost map data to show in rviz * */ void publishMap() { publish_map_.header.seq += 1; publish_map_.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); publish_map_.info = config_; map_publisher_.publish(publish_map_); } /** * @brief Publish transformation data * Necessary to transform and show map correctly in rviz */ void publishTransform() { transform_.setOrigin(tf::Vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)); quaternion_.setRPY(0.0, 0.0, 0.0); transform_.setRotation(quaternion_); // this map is generated in truck coordinate, base_link tf_broadcaster_.sendTransform( tf::StampedTransform(transform_, ros::Time(0), "base_link", "map") ); } /** * @brief Calculate index in cost map and validate whether the index is within map's size * Cost map is sorted as row major order 1D vector * @param x_m x position[m] of point cloud * @param y_m y position[m] of point cloud * @param index calculated index * @return true * @return false */ bool calculateAndValidateMapVectorIndex(float x_m, float y_m, uint32_t &index) { uint32_t i_x, i_y; i_x = getGridIndexX(x_m, config_.origin.position.x, config_.resolution); i_y = getGridIndexY(y_m, config_.origin.position.y, config_.resolution); index = getVectorIndexRowMajorOrder(i_x, i_y, config_.height); return isVectorIndexValid(index, all_cell_num_); } nav_msgs::MapMetaData config_; ros::Publisher config_publisher_; nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid publish_map_; ros::Publisher map_publisher_; tf::TransformBroadcaster tf_broadcaster_; tf::Transform transform_; tf::Quaternion quaternion_; float resolution_m_, width_m_, height_m_; float center_x_m_, center_y_m_; uint32_t all_cell_num_; float danger_likelihood_, safe_likelihood_; float height_threshold_; std::vector<CellInfo> original_map; }; #endif // _H_COST_MAP_
そしてこれが、最終的にGrid Map生成、確率更新、フィルタリングと
いう一連の処理を実行するコードです。
/** * @file point_cloud_dust_filter.cpp * @author Shisato Yano (shisatoyano@gmail.com) * @brief Class for filtering dust and noise in point cloud * @version 0.1 * @date 2022-07-02 * * @copyright Copyright (c) 2022 * */ #include "point_cloud_operation_handler.hpp" #include "point_cloud_dust_filter.hpp" PointCloudDustFilter::PointCloudDustFilter(ros::NodeHandle &nh, ros::NodeHandle &pnh) { cost_map_ = CostMap(nh, pnh); // initialize cost map // "iv_dust": topic name of filtered dust point cloud // "iv_withoud_dust" topic name of point cloud not including dust dust_publisher_ = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("iv_dust", 10); without_dust_publisher_ = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("iv_without_dust", 10); loadParameters(pnh); } void PointCloudDustFilter::operate() { updateHeightInfo(); updateOccupancyProbability(); filterDustPointCloud(); } void PointCloudDustFilter::publish() { publishCostMap(); publishPointCloud(); } void PointCloudDustFilter::loadParameters(ros::NodeHandle &pnh) { // probability threshold to detect dust and noise in point cloud // when occupancy probability is between the following min and max probability, // the data will be dust and noise pnh.getParam("min_dust_probability", min_dust_probability_); pnh.getParam("max_dust_probability", max_dust_probability_); } void PointCloudDustFilter::interpretPointCloudXYZ(uint32_t index, float &x_m, float &y_m, float &z_m) { x_m = input_pcl_.points[index].x; y_m = input_pcl_.points[index].y; z_m = input_pcl_.points[index].z; } bool PointCloudDustFilter::isDustPointCloud(uint8_t probability) { return (probability > min_dust_probability_ && probability <= max_dust_probability_); } void PointCloudDustFilter::updateHeightInfo() { float x_m, y_m, z_m; // convert subscribed point cloud from PointCloud2 of ROS to PointCloudXYZ of PCL // because it is easier to interpret pcl::fromROSMsg(input_point_cloud_, input_pcl_); for (uint32_t i_p=0; i_p < input_pcl_.size(); i_p++) { interpretPointCloudXYZ(i_p, x_m, y_m, z_m); cost_map_.updateHeightInfoInCell(x_m, y_m, z_m); } } void PointCloudDustFilter::updateOccupancyProbability() { cost_map_.updateOccupancyProbability(); } void PointCloudDustFilter::filterDustPointCloud() { pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB> dust_pcl, without_dust_pcl; float x_m, y_m, z_m; uint8_t probability; for (uint32_t i_p=0; i_p < input_pcl_.size(); i_p++) { pcl::PointXYZRGB point; interpretPointCloudXYZ(i_p, x_m, y_m, z_m); point.x = x_m, point.y = y_m, point.z = z_m; probability = cost_map_.occupancyProbability(x_m, y_m); if (isDustPointCloud(probability)) { // dust point is colored in red point.r = 255, point.g = 0, point.b = 0; dust_pcl.push_back(point); } else { // point not dust is colored in green // this is including obstacle and ground point.r = 0, point.g = 255, point.b = 0; without_dust_pcl.push_back(point); } } // convert filtered point cloud from PointCloudXYZ of PCL to PointCloud2 of ROS // to show in rviz pcl::toROSMsg(dust_pcl, dust_ros_); pcl::toROSMsg(without_dust_pcl, without_dust_ros_); } void PointCloudDustFilter::publishCostMap() { cost_map_.publish(); } void PointCloudDustFilter::publishPointCloud() { // publish dust point cloud dust_ros_.header.seq += 1; dust_ros_.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); dust_ros_.header.frame_id = "base_link"; dust_publisher_.publish(dust_ros_); // publish point cloud not including dust without_dust_ros_.header.seq += 1; without_dust_ros_.header.stamp = ros::Time::now(); without_dust_ros_.header.frame_id = "base_link"; without_dust_publisher_.publish(without_dust_ros_); } /** * @brief Main process of this Node * * @param argc * @param argv * @return int */ int main(int argc, char **argv) { ros::init(argc, argv, "point_cloud_dust_filter"); ros::NodeHandle nh; ros::NodeHandle pnh("~"); // subscribe topic "iv_trasformed_points" as input point cloud PointCloudOperationHandler handler(nh, new PointCloudDustFilter(nh, pnh), "iv_transformed_points"); // publish filtered point cloud and generated cost map handler.publishLoop(); return 0; }
まとめ
ひょんなことから久しぶりにROSを触ることになりましたが、
ちょうどLiDARの点群処理とそれによる外界認識を出来る
ようになりたいと思ってたので、その手法を学び、初めて
自分の手でフルスクラッチ実装できて良かったです。
ただし、まだまだ雰囲気で良く理解できていないままやってる感が
否めないので、今後も学習を続けていこうと思います。
